Transport of Gases
Transport of Gases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Transport of Gases, Transport of Oxygen, Haemoglobin, Oxyhaemoglobin, Oxygen Dissociation Curve, Transport of Carbon Dioxide & Carbamino-haemoglobin etc.
Important Questions on Transport of Gases
The majority of carbon dioxide produced by our body cells is transported to the lungs
The carbon dioxide is transported via blood to lungs as:
Oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin is
Carbon dioxide is transported from tissue to respiratory surface by only
Blood analysis of a patient reveals an unusually high quantity of carboxyhaemoglobin content. Which of the following conclusions is most likely to be correct?
"The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of ___________________."
CO2 is transported through the blood to the lungs in the form (s) as
The oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve will show a right shift in case of
is dissolved in haemoglobin or blood plasma as
Acquiring an oxygen debt is evidence that
Oxygen is transported to every cell of the body through
What is the maximum number of oxygen atoms that a molecule of haemoglobin can bind?
A sigmoid curve is obtained when percentage saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen is plotted against the as indicated below:
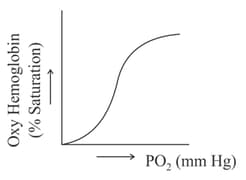
If a patient who is a hypothermic with a body temperature of the curve shifts towards
Left side shift of oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve occurs during
Which of the following statement is correct?
Which statements are true/false?
(i) Blood transports comparatively easily because of its high solubility.
(ii) Approximately of is transported dissolved in plasma.
(iii) diffuses into blood, passes into , and reacts with water to form .
(iv) Oxyhaemoglobin of erythrocytes is basic.
(v) Chloride ions diffuse from plasma into erythrocytes to maintain ionic balance.
The amount of oxygen present in one gram of haemoglobin is
What is true about in humans?
Percentage of oxygen being carried by blood plasma is
Dissociation curve of O2 (which is dissociation from Hb) shifts to the right when
Bicarbonate formed inside erythrocytes moves out to plasma while chloride of plasma pass into erythrocytes. The phenomenon is called
